The #1 tip that I can give is to use the automatic tools for your data preparation, they are free, open source and use open data.
For more information about the automatic tools available to you, please review the Making Evaluation Maps article.
Background information
- Please review supported data formats article and the attributes required for evaluation maps. Geodesignhub only supports GeoJSON for adding externally prepared data into evaluations and constraints and diagrams.
- Please review the supported map projection. Any other projection is not supported.
- If data is created in Shapefiles / Geopackage, it has to be converted into GeoJSON before uploading, native uploading of Shapefiles is not supported. Review the converting data to GeoJSON article
What kind of map am I making?
GIS data can be added into a diagram, evaluation, or impact maps. Identify what type of file you are creating:
- Evaluation map
- Impact map or
- diagram
If you have a lot of time or budgets for map making, using the automatic tools will dramatically simplify your job from making the maps to reviewing maps. If you cannot use the tools, we can make the maps for you.
Review data attributes
If you do decide to make your own maps, once you have identified the type of file that you are creating, please review the attributes required for the type of data that is being uploaded.
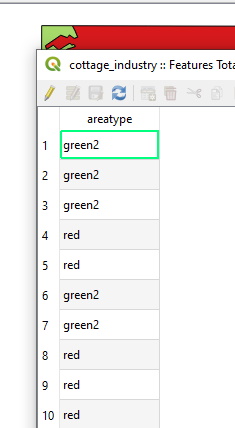
In the case of evaluation maps, every polygon feature must have a column named areatype and it must be one of the following values:
- red
- yellow
- green
- green2
- green3
It is recommended that you remove all other attributes from the file in this process.
The screenshot below shows a example attribute table with only the areatype column.
Geometry tip #1: Simplify multi-part geometry
If you have a MultiPolygon geometry, it is recommended that you “explode” the features so that it contains single part geometry. The “Multipart to Singlepart” command in QGIS is most useful here.
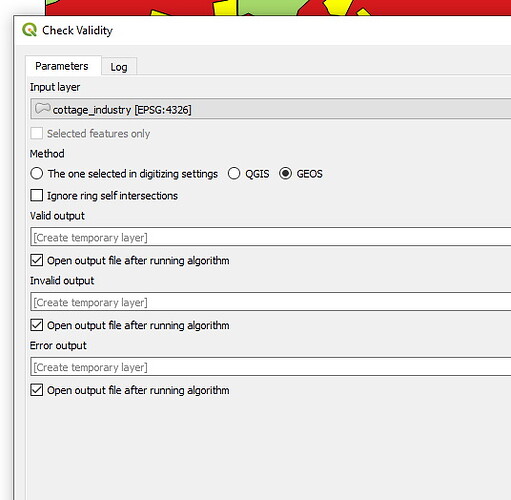
Geometry tip #2: Check geometry validity
Once you have removed all extra attributes and appropriately classified the polygons in the file as being one of the allowed attributes, the next step is to check geometry validity. This is to ensure that the calculations are correct and consistent.
Remove all geometry errors either manually or if too many then simplify the file and re run the tool. Sometimes dissolving features may help in reducing the geometry validity errors.
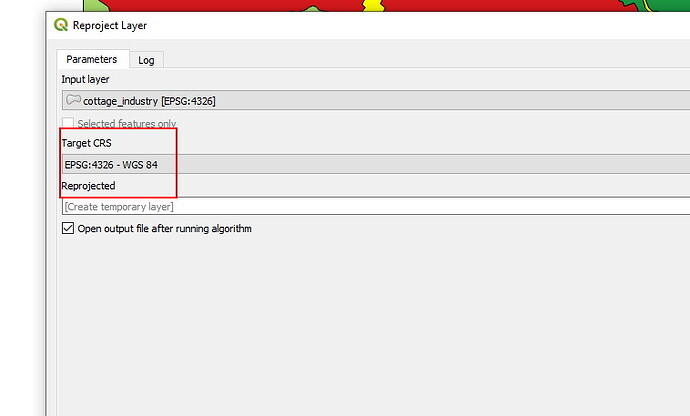
Geometry tip #3: Re-project your data
Convert the shape-file projection to EPSG 3857 projection. All data on the site uses this projection, please refer to our Data Projection article.
Geometry tip #4: Convert to GeoJSON
GeoJSON supports precision upto 6 decimal places so you might want to consider simplifying features. If the file size of the resulting GeoJSON is large >4MB, you will need to simplify the features. Please review the features simplification topic for further information.
Geodesignhub Evaluation Maps Converter
A online tool Geodesignhub Evaluation Maps converter now exists to help you reproject and convert your GeoPackage so that it can be directly uploaded to the tool. Your Evaluation file must still have the areatype column in the attribute table with the correct attributes as mentioned above.
Geometry tip #4: Convert to GeoJSON
GeoJSON supports precision upto 6 decimal places so you might want to consider simplifying features. If the file size of the resulting GeoJSON is large >4MB, you will need to simplify the features. Please review the features simplification topic
Geometry tip #5: Dissolve adjacent polygons using areatype
Use the Dissolve by attribute feature in QGIS to dissolve adjacent polygons of the same “areatype”.